
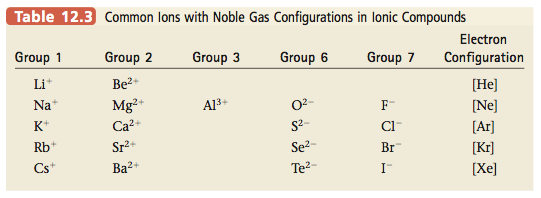
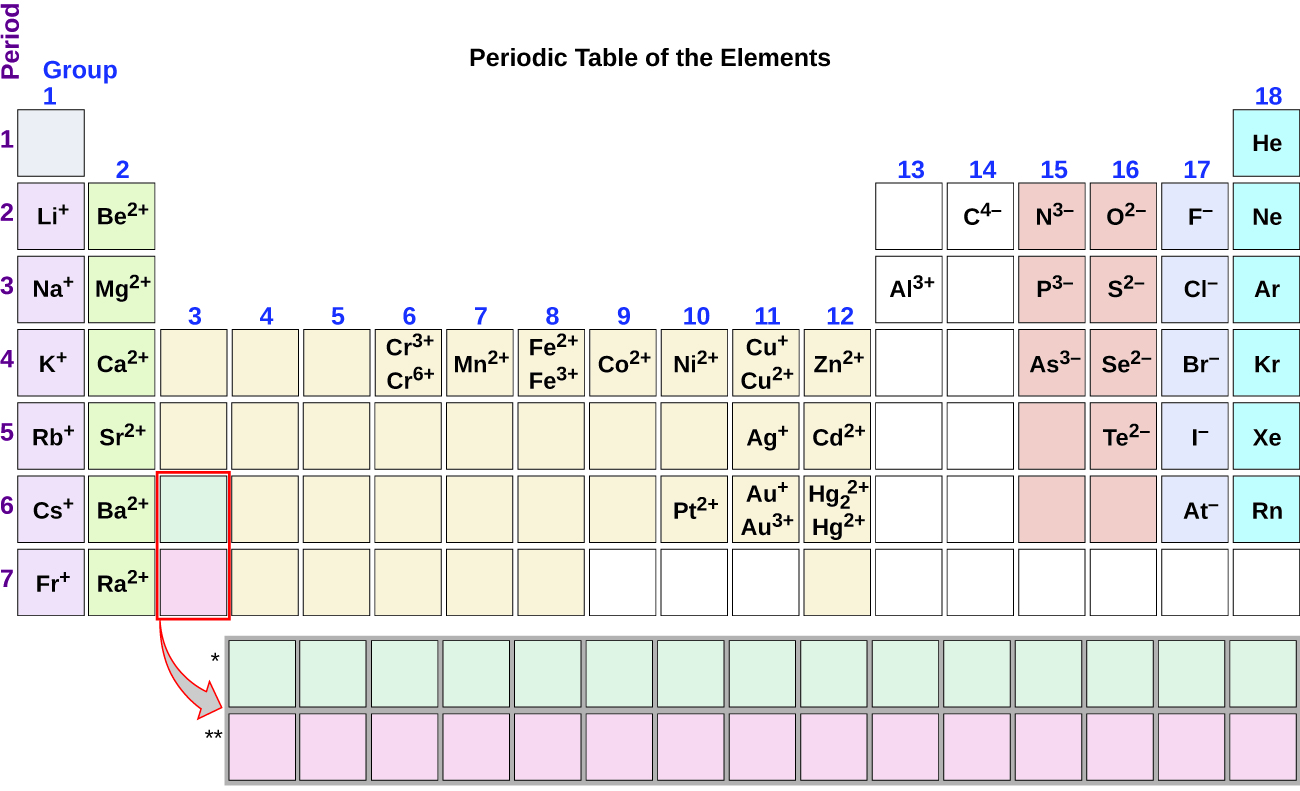
Lead, mercury (II), and silver sulfate are slightly soluble.Copper (I) halides are insoluble, although this exception is usually not listed in standard solubility rules.Bromates and formates are generally soluble.This allows minerals to be separated by density. It has possibly the highest density of an aqueous solution. A Clerici solution is a solution of equal parts thallium formate and thallium malonate, both extremely soluble.Rubidium formate, thallium formate, and silver perchlorate are 3 of the most highly soluble compounds, with over 5,000 grams of each dissolving in a liter of water at room temperature!.Sodium acetate is so soluble in water, that it can be difficult to form a supersaturated solution.This can be used to separate potassium from sodium in a solution. Potassium chlorate, bromate, and perchlorate are only slightly soluble in cold water.Interesting Solubility Facts & Exceptions A magnetic stirrer is often run to help speed things up. For example, crystals of copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate seem to take forever to dissolve. Some compounds can take a while to dissolve. The solubility product constant, known as the Ksp value, allows you to calculate how much will actually dissolve. For example, potassium bromate is quite soluble in hot water, but only slightly soluble in very cold water.Įven the most insoluble ionic compounds will dissolve into ions to a very small degree. Some compounds can have very different solubilities in hot or cold water. The solubility rules in this article are in water at room temperature.
Supernate – the solution that is left after a precipitate is removed or filtered out.Solvent – the liquid that dissolves your compound.This is done usually by forming a saturated solution in hot water, and then letting the solution very slowly cool without any seed crystals present Supersaturated solution – one that has more than the maximum dissolved.Saturated solution – a solution that has the maximum amount of the compound dissolved into solution.Coffee filter – a great way to separate your precipitate from the solution!.Precipitate – what comes out of solution when a compound that is formed is not soluble.Soluble – more than 30 grams dissolve in a liter.Sparingly soluble 10-30 grams dissolves in a liter.Slightly soluble 1-10 grams dissolves in a liter.Insoluble – less than 1 gram dissolves in a liter.Let’s discuss solubility and some terms associated with it. Fluorides are insoluble, except for the alkali metals and NH₄⁺.Phosphates are insoluble, except for the alkali metals and NH₄⁺.Chromates are insoluble, except for the alkali metals and NH₄⁺.Carbonates are insoluble, except for the alkali metals and NH₄⁺.Sulfides are highly insoluble, except for the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals.Hydroxides are insoluble, except for the alkali metals which are soluble, and the alkaline earth metals Mg +2, Ca +2, Sr +2, Ba +2 which are slightly soluble.Sulfates are soluble, except for Ca +2, Sr +2, Ba +2, Pb +2, and Ag +2.Silver compounds are insoluble, except for silver nitrate and silver acetate.Chlorides, bromides and iodides are soluble, except for Ag +, Pb +2, and Hg 2 +2.

So are acetates, chlorates and perchlorates.
#Sr element common ion plus
Salts of the alkali metals, plus NH4 +, are usually soluble.If all combinations of ions are soluble, then no precipitate will form, and you will often be unable to isolate a single compound. These solubility rules can help you predict if a precipitate will form when two ionic compounds are mixed in a solution. We will also display a solubility chart that states the solubility of many common ionic compounds.
In this article, we look at the common solubility rules of chemistry, which state which anions and cations are usually soluble, and which aren’t. Watching a colorful precipitate form, or redissolve, can be very exciting. Solubility is one of most interesting parts of chemistry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
